Designers often struggle with repetitive geometry setup, bounding box calculations, and precise alignment when building modular layouts in Cinema 4D. This Python generator script addresses these pain points by introducing smart bounds detection, dynamic spline creation, and automatic alignment to linked objects—all wrapped in a single, artist-friendly tool.
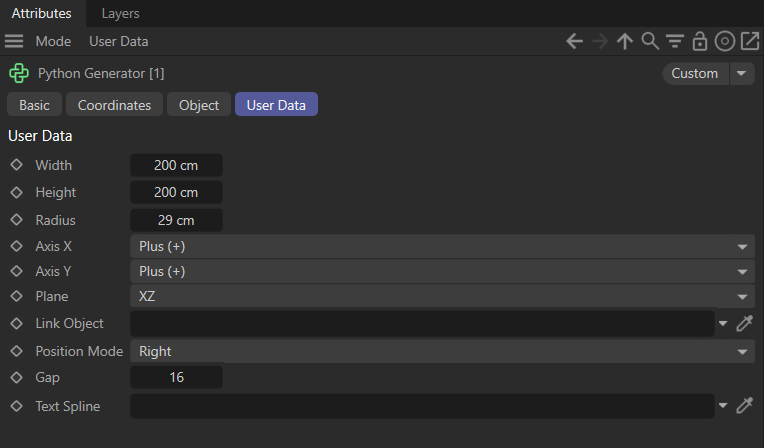
What This Script Does
- Smart Bounds Calculation The
get_smart_bounds()function intelligently computes the bounding box of any object, even if it has children or cached geometry. This ensures accurate size and position data without manual guesswork. - Customizable Rectangle Generator Designers can define width, height, corner radius, alignment, and gap spacing through user data fields. The script automatically draws a closed Bezier spline that represents the rectangle, with optional rounded corners.
- Multi‑Plane Flexibility The spline can be drawn on XY, XZ, or YZ planes, making it versatile for 2D layouts, floor plans, or vertical arrangements.
- Automatic Alignment to Linked Objects By linking another object, the generator positions itself relative to that object’s bounds. Whether you want it to sit to the left, right, above, or below, the script handles the math and keeps everything visually consistent.
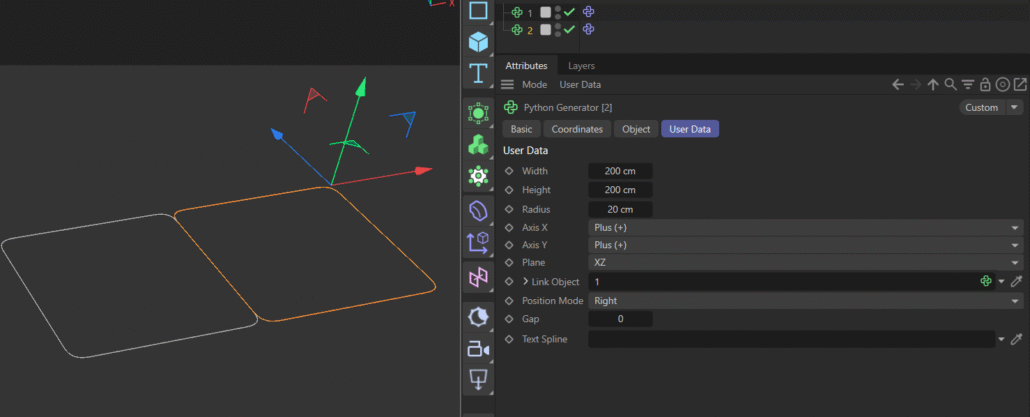
🎨 Benefits for Designers
- Faster Layouts: No need to manually measure or align splines—geometry adapts instantly.
- Reusable Automation: Once set up, the generator can be reused across projects, saving hours of repetitive work.
- Precision Control: Rounded corners, gaps, and alignment modes give designers pixel‑perfect control over spline visuals.
- Adaptive Positioning: Linking to other objects ensures your design stays modular and responsive to changes.
- Artist‑Friendly Workflow: The script is built around user data fields, meaning designers can tweak parameters without touching code.
🛠 Example Use Cases
- UI Mockups: Generate rounded rectangles for interface elements directly inside Cinema 4D.
- Motion Graphics: Create spline‑based shapes that can drive animations, extrusions, or effectors.
- Architectural Layouts: Quickly block out floor plans or modular structures with precise bounding boxes.
- Packaging Design: Align spline guides to product geometry for accurate dielines and cut paths.
🚀 Why It Matters
This script bridges the gap between technical precision and creative freedom. Instead of wasting time on manual bounding box adjustments, designers can focus on the artistry of their layouts. By automating repetitive geometry tasks, it empowers motion designers, 3D artists, and creative coders to work smarter, not harder.
Python
Download “Smart_Plane_Cinema_4D_Python_Generator” Smart_Plane_Cinema_4D_Python_Generator.zip – Downloaded 0 times – 27.60 KB
import c4d
# --- 1. SMART BOUNDS ---
def get_smart_bounds(obj):
if not obj: return c4d.Vector(0), c4d.Vector(0), c4d.Matrix()
if obj.GetGUID() == op.GetGUID(): return c4d.Vector(0), c4d.Vector(0), c4d.Matrix()
mg = obj.GetMg()
rad = obj.GetRad()
mp = obj.GetMp()
cache = obj.GetCache()
if cache:
return cache.GetMg() * cache.GetMp(), cache.GetRad(), obj.GetMg()
if rad.x < 0.001:
children = obj.GetChildren()
if children:
min_v = c4d.Vector(1e15)
max_v = c4d.Vector(-1e15)
has_child = False
for child in children:
cmg = child.GetMg()
crad = child.GetRad()
if crad.x < 0.001 and child.GetCache():
crad = child.GetCache().GetRad()
for i in range(8):
vx = crad.x if (i&1) else -crad.x
vy = crad.y if (i&2) else -crad.y
vz = crad.z if (i&4) else -crad.z
p_global = cmg * (child.GetMp() + c4d.Vector(vx,vy,vz))
p_local = ~mg * p_global
min_v.x = min(min_v.x, p_local.x)
max_v.x = max(max_v.x, p_local.x)
min_v.y = min(min_v.y, p_local.y)
max_v.y = max(max_v.y, p_local.y)
has_child = True
if has_child:
mp = (min_v + max_v) * 0.5
rad = (max_v - min_v) * 0.5
return mg * mp, rad, mg
def main():
# 1. GET DATA (Only IDs 1 through 9)
try:
width = op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 1]
height = op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 2]
radius = op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 3]
align_x = int(op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 4])
align_y = int(op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 5])
plane = int(op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 6])
link_obj = op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 7]
pos_mode = int(op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 8])
gap = op[c4d.ID_USERDATA, 9]
except:
width, height, radius, gap = 200.0, 100.0, 0.0, 0.0
align_x, align_y, plane, link_obj, pos_mode = 0, 0, 0, None, 0
# 2. CALCULATE VISUALS
draw_w = max(0, width - gap)
draw_h = max(0, height - gap)
max_rad = min(draw_w, draw_h) / 2.0
if radius > max_rad: radius = max_rad
if radius < 0: radius = 0
# Axis Offsets (Shifting the visual box relative to 0,0)
start_x = 0.0
if align_x == 0: start_x = -width / 2.0
elif align_x == 2: start_x = -width
start_y = 0.0
if align_y == 0: start_y = -height / 2.0
elif align_y == 2: start_y = -height
# VISUAL CENTER (Local)
vis_center_x = start_x + (width / 2.0)
vis_center_y = start_y + (height / 2.0)
# 3. DRAW SPLINE
l, r = vis_center_x - (draw_w/2), vis_center_x + (draw_w/2)
b, t = vis_center_y - (draw_h/2), vis_center_y + (draw_h/2)
li, ri, bi, ti = l+radius, r-radius, b+radius, t-radius
verts = [
c4d.Vector(r, bi, 0), c4d.Vector(r, ti, 0),
c4d.Vector(ri, t, 0), c4d.Vector(li, t, 0),
c4d.Vector(l, ti, 0), c4d.Vector(l, bi, 0),
c4d.Vector(li, b, 0), c4d.Vector(ri, b, 0)
]
if plane == 1: verts = [c4d.Vector(v.x, 0, v.y) for v in verts]
elif plane == 2: verts = [c4d.Vector(0, v.y, v.x) for v in verts]
spline = c4d.SplineObject(8, c4d.SPLINETYPE_BEZIER)
spline[c4d.SPLINEOBJECT_CLOSED] = True
spline.SetAllPoints(verts)
if radius > 0.001:
k = radius * 0.55228475
tx, ty, tz = c4d.Vector(k,0,0), c4d.Vector(0,k,0), c4d.Vector(0,0,k)
tu, td, tr, tl = c4d.Vector(0), c4d.Vector(0), c4d.Vector(0), c4d.Vector(0)
if plane == 0: tu, td, tr, tl = ty, -ty, tx, -tx
elif plane == 1: tu, td, tr, tl = tz, -tz, tx, -tx
elif plane == 2: tu, td, tr, tl = ty, -ty, tz, -tz
spline.SetTangent(0, td, c4d.Vector(0)); spline.SetTangent(1, c4d.Vector(0), tu)
spline.SetTangent(2, tr, c4d.Vector(0)); spline.SetTangent(3, c4d.Vector(0), tl)
spline.SetTangent(4, tu, c4d.Vector(0)); spline.SetTangent(5, c4d.Vector(0), td)
spline.SetTangent(6, tl, c4d.Vector(0)); spline.SetTangent(7, c4d.Vector(0), tr)
# 4. POSITIONING GENERATOR (SELF-ALIGNMENT TO LINK)
if link_obj:
link_center, link_rad, link_mg = get_smart_bounds(link_obj)
my_rad_x = width / 2.0
my_rad_y = height / 2.0
offset_vec = c4d.Vector(0)
if pos_mode == 0: offset_vec = c4d.Vector(link_rad.x + my_rad_x, 0, 0)
elif pos_mode == 1: offset_vec = c4d.Vector(-(link_rad.x + my_rad_x), 0, 0)
elif pos_mode == 2: offset_vec = c4d.Vector(0, link_rad.y + my_rad_y, 0)
elif pos_mode == 3: offset_vec = c4d.Vector(0, -(link_rad.y + my_rad_y), 0)
target_geo_center = link_center + link_mg.MulV(offset_vec)
my_internal_offset = c4d.Vector(vis_center_x, vis_center_y, 0)
if plane == 1: my_internal_offset = c4d.Vector(vis_center_x, 0, vis_center_y)
elif plane == 2: my_internal_offset = c4d.Vector(0, vis_center_y, vis_center_x)
target_mg = c4d.Matrix(link_mg)
rotated_internal_offset = target_mg.MulV(my_internal_offset)
target_mg.off = target_geo_center - rotated_internal_offset
if (op.GetMg().off - target_mg.off).GetLength() > 0.001:
op.SetMg(target_mg)
return spline